Best Zero Trust sources Microsoft 365 + Azure
Hi! I’ve merged great Microsoft content in one article and provided the greatest screenshots or links to valuable content. Happy reading! If you have other useful sources give a comment.
Also read: How to build your Zero Trust workplace with Microsoft 365
Microsoft’s approach to Zero Trust Networking and supporting Azure technologies
02:19 An overview of Microsoft’s environment
03:28 Cloud networking – by the numbers
06:22 Initiative alignment
09:32 Microsoft enterprise networking 2020
12:25 Elements of Zero Trust networking
15:45 Does Microsoft benchmark against industry models for Zero Trust to stay ahead of the practice?
17:42 Zero Trust networking maturity model
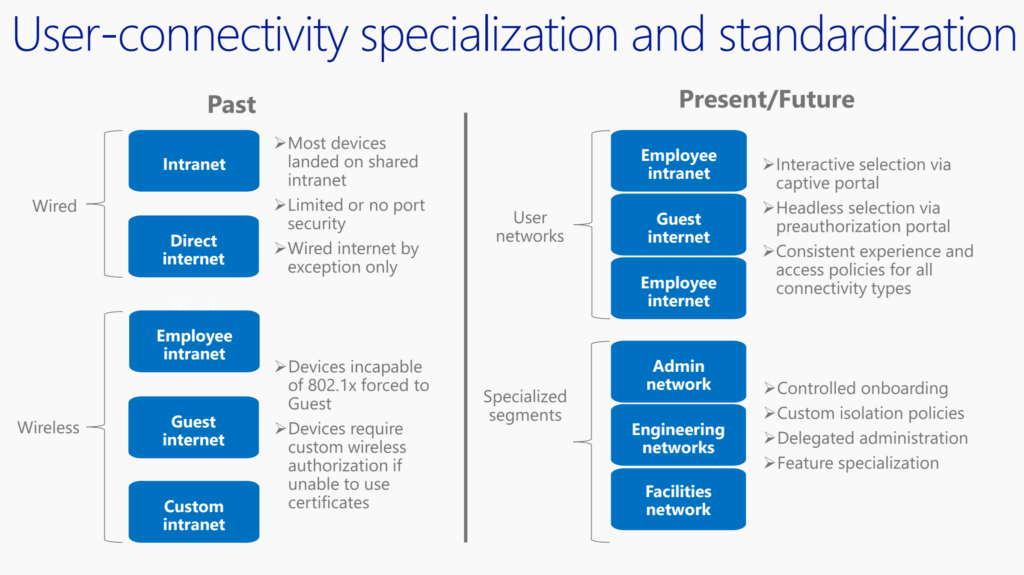
19:27 User-connectivity specialization and standardization
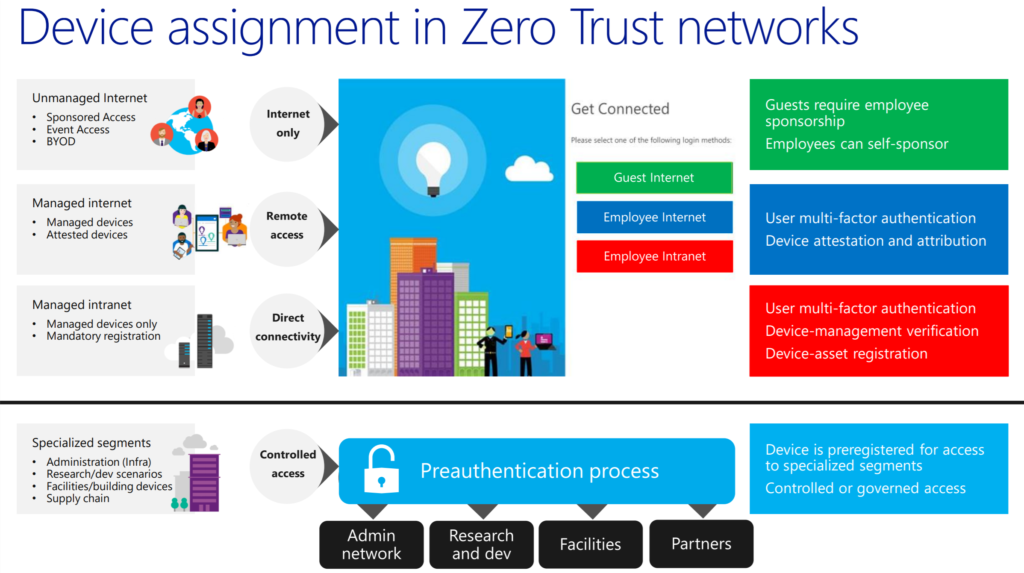
26:20 Device assignment in Zero Trust networks
31:22 Locking down our “open” cloud and datacenter networks
40:29 Future scenario: leveraging native Azure services
44:09 Future scenario: connectivity via Azure virtual WAN
49:31 Future scenario: Infrastructure as Code
53:07 Key takeaways
Zero Trust with Microsoft Services (showcase)
Zero Trust access architecture addresses the modern security challenges that come with cloud migration and a mobile workforce. By implementing Zero Trust, Microsoft takes a layered approach to secure corporate and customer data. Microsoft’s phased implementation of Zero Trust centers on strong user identity, device health verification, validation of application health, and secure, least-privilege access to corporate resources and services.

https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/itshowcase/implementing-a-zero-trust-security-model-at-microsoft
Zero Trust business model
Link.
Microsoft Blogs (general information)
How to organize your security team: The evolution of cybersecurity roles and responsibilities

Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) Workshop Training (5 modules)

Module 1: Microsoft Cybersecurity Briefing: This module covers overviews on critical security hygiene, Microsoft cybersecurity reference architecture, cybersecurity resilience, Internet of Things (IoT), and operational tech.
Module 2: Security Management: Learn how to increase visibility and control over your hybrid enterprise estate with integrated guidance, automated policy enforcement, and monitoring.
Module 3: Identity and Zero Trust User Access: Learn how to advance zero trust with your identity and user access strategy to better protect corporate data inside and outside your network perimeter
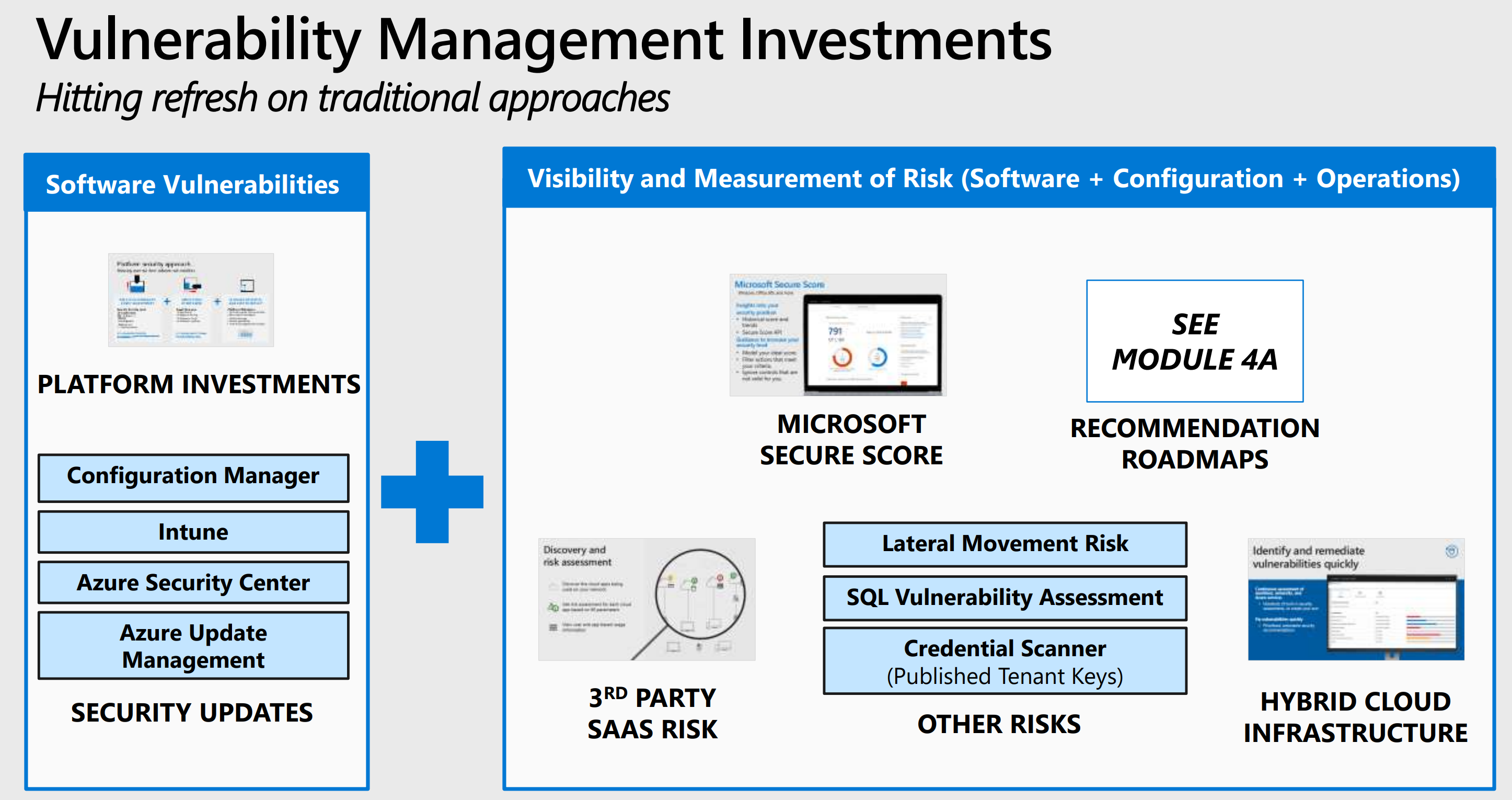
Module 4a: Threat Protection Strategy, Part I: Explore key learnings about threat protection, security evolution, strategies, and security road maps.
Module 4b: Threat Protection Strategy, Part II: This module reviews the evolution and trajectory of the Security Operations Centers (SOC), powered by the trillions of signals in the Microsoft Intelligent Security Graph.
Module 5: Information Protection: Learn how to protect sensitive information wherever it goes with automatic classification, persistent encryption across devices, and continuous monitoring of data across mobile devices, cloud services, and other corporate assets.
Downloads
- Module 1: Microsoft Cybersecurity Briefing PDF
- Module 1: Microsoft Cybersecurity Briefing PPT
- Module 2: Security Management PDF
- Module 2: Security Management PPT
- Module 3: Identity and Zero Trust User Access PDF
- Module 3: Identity and Zero Trust User Access PPT
- Module 4a: Threat Protection Strategy PDF
- Module 4a: Threat Protection Strategy PPT
- Module 4b: Threat Protection Strategy PDF
- Module 4b: Threat Protection Strategy PPT
- Module 5: Information Protection PDF
- Module 5: Information Protection PPT
Vision Paper
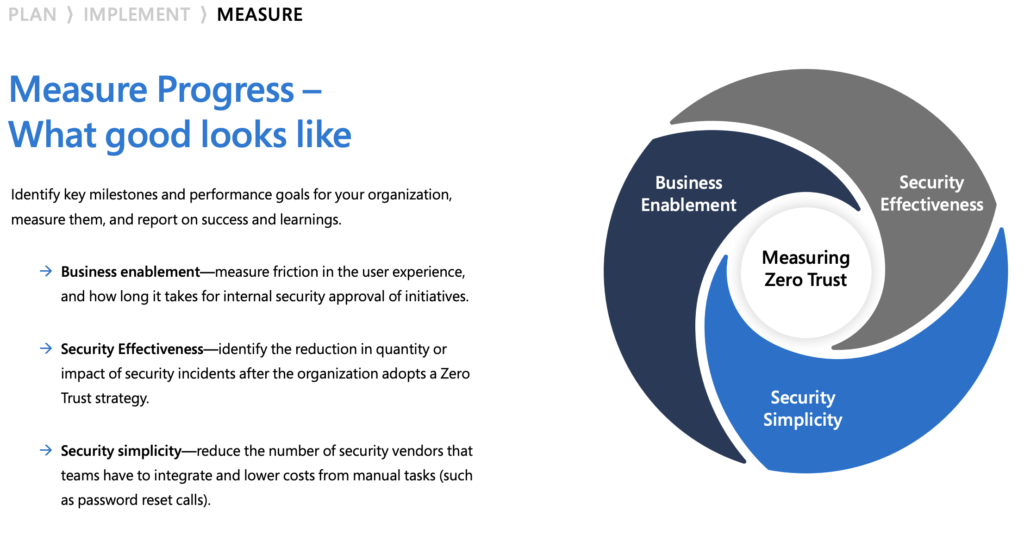
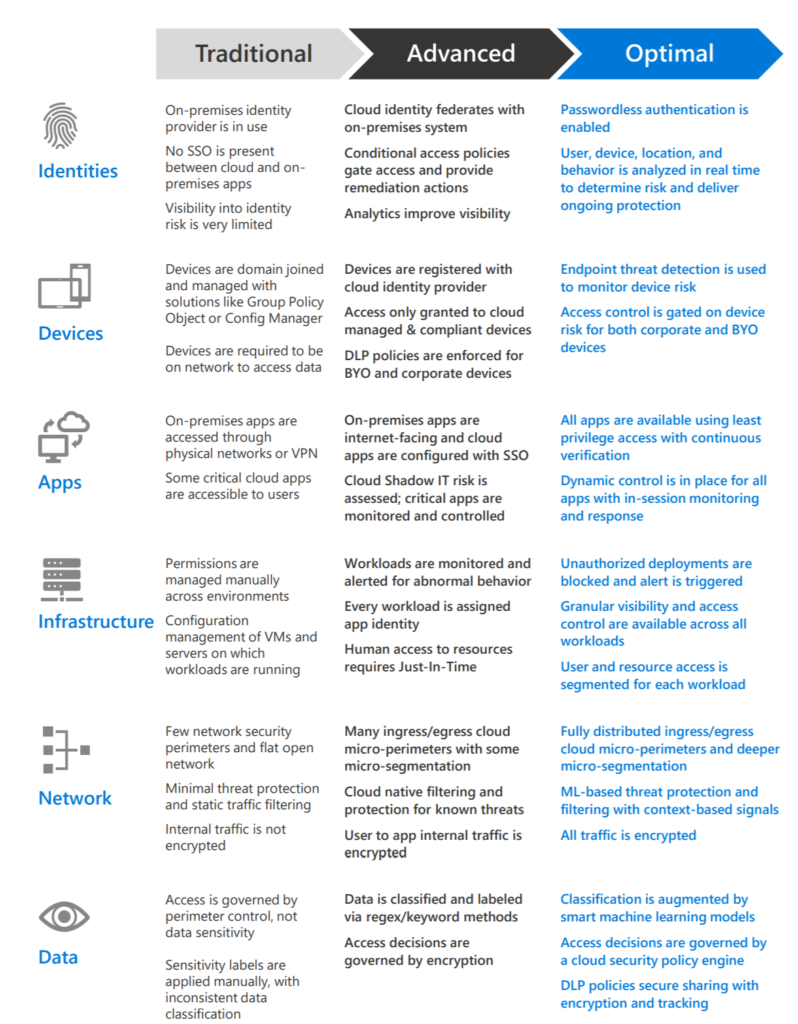
Different organizational requirements, existing technology implementations, and security stages all affect how a Zero Trust security model implementation is planned. Using our experience in helping customers to secure their organizations as well as implementing our own Zero Trust model, we’ve developed the following maturity model to help you assess your Zero Trust readiness and build a plan to get to Zero Trust.
Zero Trust: A new era of security Ebook

Microsoft Digital Defence Report

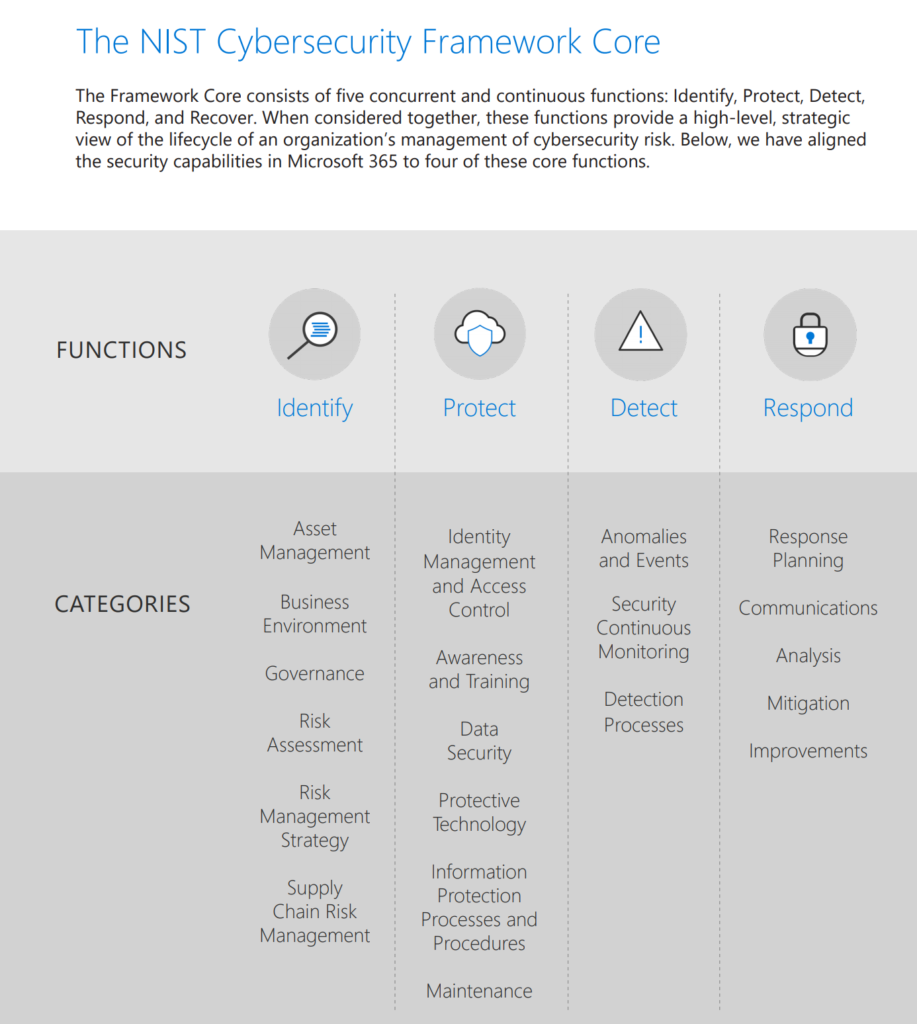
Microsoft 365 + the NIST cybersecurity framework
Zero trust landing page
General: microsoft.com/en-us/security/business/zero-trust
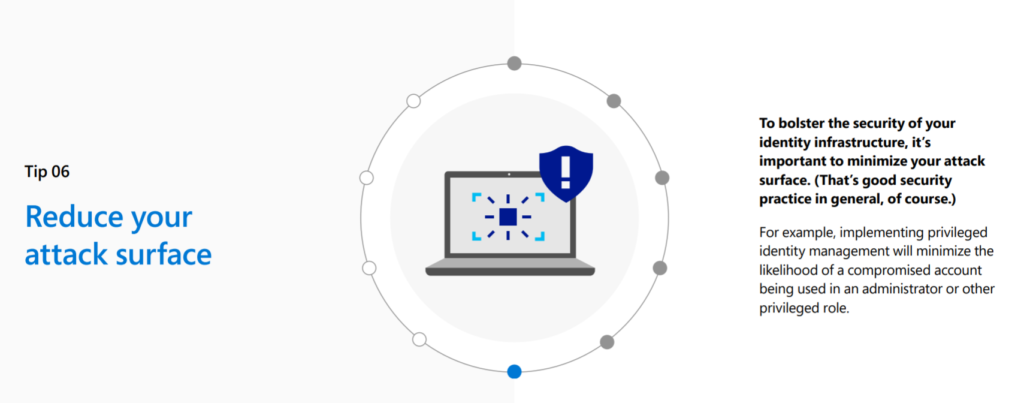
Maturity paper and 10 tips for enabling zero trust security
Azure: Overview of the security pillar
| Security Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Role of security | Security is one of the most important aspects of any architecture. Security provides confidentiality, integrity, and availability assurances against deliberate attacks and abuse of your valuable data and systems. |
| Security design principles | These principles support these three key strategies and describe a securely architected system hosted on cloud or on-premises datacenters (or a combination of both). |
| Types of attacks to resist | An architecture built on good security practices should be resilient to attacks. It should both resist attacks and recover rapidly from disruption to the security assurances of confidentiality, integrity, and availability. |
| Regulatory compliance | Governments and other organizations frequently publish standards to help define good security practices (due diligence) so that organizations can avoid being negligent in security. |
| Reduce organizational risk | Much like physical safety, success in information security is defined more as an ongoing task of applying good security practices and principles and hygiene rather than a static absolute state. |
| Administration | Administration is the practice of monitoring, maintaining, and operating Information Technology (IT) systems to meet service levels that the business requires. Administration introduces some of the highest impact security risks because performing these tasks requires privileged access to a very broad set of these systems and applications. |
| Applications and services | Applications and the data associated with them ultimately act as the primary store of business value on a cloud platform. |
| Governance, risk, and compliance | How is the organization’s security going to be monitored, audited, and reported? What types of risks does the organization face while trying to protect identifiable information, Intellectual Property (IP), financial information? Are there specific industry, government, or regulatory requirements that dictate or provide recommendation on criteria that your organization’s security controls must meet? |
| Identity and access management | Identity provides the basis of a large percentage of security assurances. |
| Info protection and storage | Protecting data at rest is required to maintain confidentiality, integrity, and availability assurances across all workloads. |
| Network security and containment | Network security has been the traditional linchpin of enterprise security efforts. However, cloud computing has increased the requirement for network perimeters to be more porous and many attackers have mastered the art of attacks on identity system elements (which nearly always bypass network controls). |
| Security Operations | Security operations maintain and restores the security assurances of the system as live adversaries attack it. The tasks of security operations are described well by the NIST Cybersecurity Framework functions of Detect, Respond, and Recover. |
Microsoft Zero Trust deployment guide for your applications

Tools to drive your Zero Trust implementation
- Strong authentication. Ensure strong multi-factor authentication and session risk detection as the backbone of your access strategy to minimize the risk of identity compromise.
- Policy-based adaptive access. Define acceptable access policies for your resources and enforce them with a consistent security policy engine that provides both governance and
insight into variances. Micro-segmentation. Move beyond simple centralized network-based perimeter to comprehensive and distributed segmentation using software-defined micro-perimeters. - Automation. Invest in automated alerting and remediation to reduce your mean time to respond (MTTR) to attacks.
- Intelligence and AI. Utilize cloud intelligence and all available signals to detect and respond to access anomalies in real time.
- Data classification and protection. Discover, classify, protect, and monitor sensitive data to minimize exposure from malicious or accidental exfiltration
Zero Trust Deployment Center
Secure identity with Zero Trust — https://aka.ms/ZTIdentity
Secure endpoints with Zero Trust — https://aka.ms/ZTDevices
Secure applications with Zero Trust — https://aka.ms/ZTApplications
Secure data with Zero Trust — https://aka.ms/ZTData
Secure infrastructure with Zero Trust — https://aka.ms/ZTInfrastructure
Secure networks with Zero Trust — https://aka.ms/ZTNetwork
Visibility, automation, and orchestration with Zero Trust — https://aka.ms/ZTCrossPillars
Zero Trust Deployment Center – https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/security/zero-trust/
Microsoft 365 for IT Architects
- Microsoft Teams and related productivity services in Microsoft 365 for IT architects
- Groups in Microsoft 365 for IT Architects
- Microsoft 365 information protection and compliance capabilities
- Security and Information Protection for Multi-Region Organizations
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint deployment strategy
- Identity and device protection for Microsoft 365
- Advanced eDiscovery architecture in Microsoft 365
- Microsoft Telephony Solutions
Thank you for reading my summary of great places to find Zero Trust information. If you have great sources please put them in the comment.
Jasper